The Anatomy of the Google Search Results
The Anatomy of the Google Search Results
Get weekly
HubSpot Updates
The Google search engine has been around since the late 1990s, and the chances are you’re a regular user. After all, Google enjoys a 75.2% search market share over it’s rivals.
You might even use it every day, but do you actually understand the makeup of a Google search result page? You might not think it matters, but if you’re hoping to maximise your organisation’s presence on the world’s most popular search engine it is important to know what you’re dealing with.
A typical search result page
Please note that not all of the search result features we’re going to talk about in this blog will appear in every search you conduct.Let’s conduct a fairly standard search for ‘boiler repairs Milton Keynes’.
Paid listings
After hitting the enter button, the first thing you’ll see at the very top of the page are the paid listings. There will be a maximum of four (dependent on how many brands are bidding on that particular term) and are identifiable by the little ‘Ad’ label alongside them.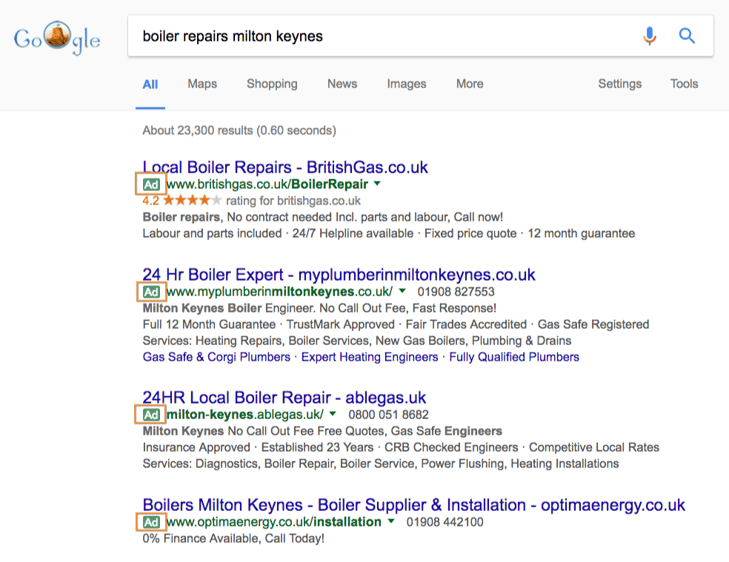
Until recently, there was just a maximum of three paid ads at the top of the SERPs (search engine results pages) as well as ads that ran down the right-hand side. The change meant that there were fewer ads on a SERP, but that the organic listings were shifted further down the page for the most competitive searches.
Map listings
Below the paid listings on our SERP for ‘boiler repairs Milton Keynes’ is the local map listings.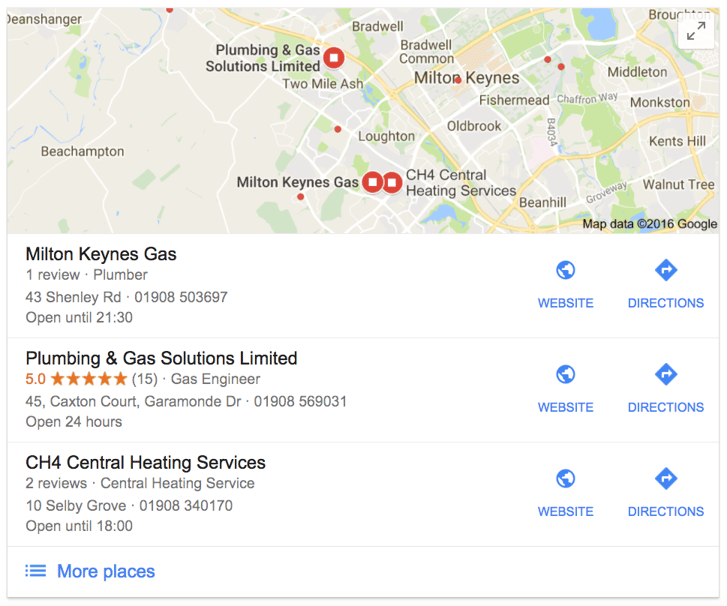
Here we can see some of the local businesses that can help with boiler repairs, as well as where they’re based specifically. You can click on ‘More places’ to be taken through to the Google Maps page for this search, providing a longer list of MK-based businesses as well as a larger map.
The map listings don’t appear on every search, but we’re seeing them on this one because there is a specific local intent. The fact we’ve searched for ‘boiler repairs Milton Keynes’ tells Google that we want to see companies that serve the town, and therefore understands that we also probably want to see companies that are locally based.
However, the map results would also appear even if we simply searched for ‘boiler repairs’. This is because Google knows our location and assumes that, for a service such as this, we want to find local businesses.
Organic listings
Ranking organically in position one on page one used to be the Holy Grail, but nowadays the organic listings begin so far down the page it’s not the click-through guarantee that it used to be.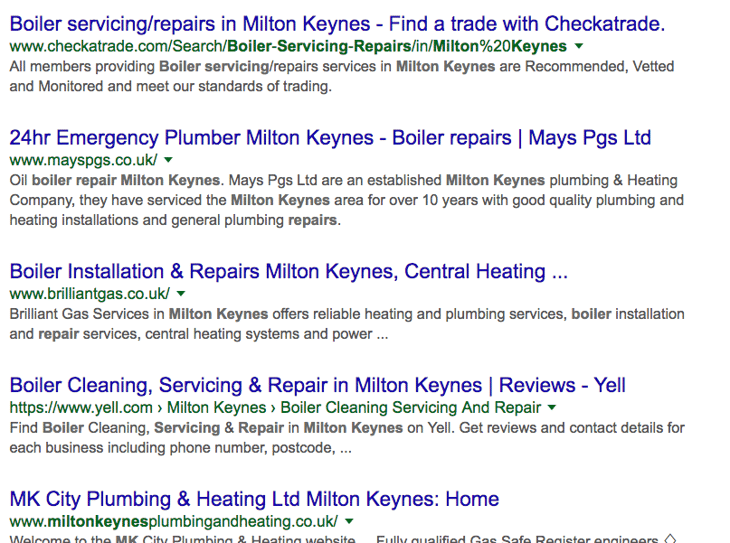
There will, typically, be ten organic listings, however this will sometimes be fewer depending on the presence of additional SERP features, but we’ll come to those shortly.
Paid listings… again.
Finally, for many searches there will be further ads below the organic listings. Here you’ll find a maximum of three, again depending on the competitiveness of the search.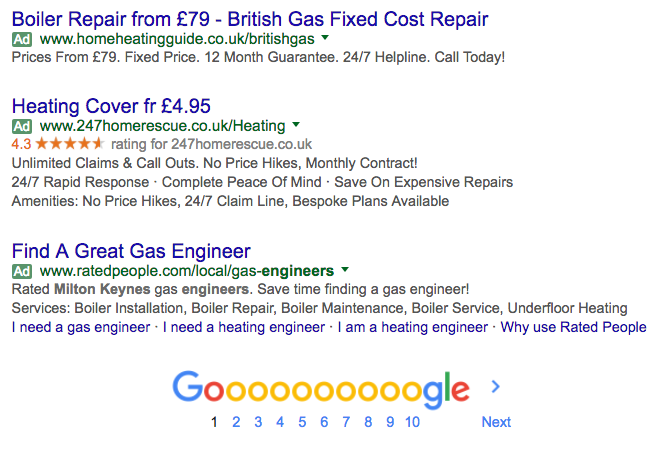
Search ‘Tools’
The appearance of the SERPs will differ slightly depending on how you word your searches — for example, ‘boiler repair MK’ will return slightly different results to ‘boiler repairs milton keynes’ — but to more significantly affect the results you see you can use the ‘Tools’ just below the search bar.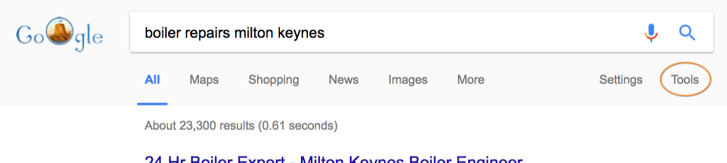
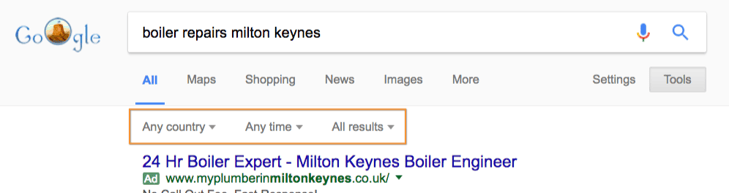
Clicking that button will reveal a few different search options:
- country;
- time; and
- a choice between ‘All Results’ and ‘Verbatim’.
Country
We have two options to choose from here: ‘Any country’ or ‘Country: the UK’.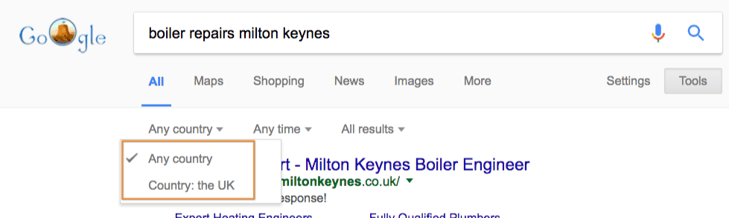
Previously, searchers were able to change their location, but Google dropped this feature last December meaning you can now either search for results from anywhere in the world or specific to the country you’re in.
For the most part Google will usually provide search results that are relevant to the country you’re from anyway. However, if you conducted a search that could be feasibly answered by websites from any country, but you know that the answer will differ depending on the country the website originates from, you should set this to ‘Country: the UK’.
Time
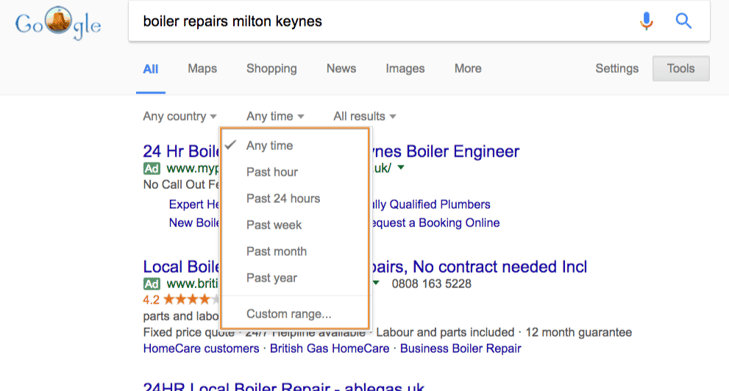
If you only want to find results from a particular time frame, this is the option for you.
This wouldn’t be relevant for our type of example search, but if, for example, you want to find a guide to using Microsoft Excel, you’d probably want to find an up-to-date article (assuming your version of Excel is up-to-date). For this, you might change the setting to ‘Past month’ or ‘Past year’.
You can also set custom ranges if you wanted to find content on a subject from a specific time period.
Verbatim search
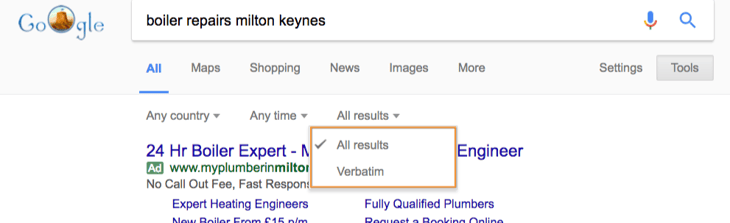 When you conduct a search on Google the search engine applies a whole load of thinking beyond simply looking up results that match your search term.
When you conduct a search on Google the search engine applies a whole load of thinking beyond simply looking up results that match your search term.
The algorithm considers:
- Personalisation, for example what websites have you visited previously.
- Corrections if Google thinks you’ve misspelled a word within your search.
- Related search results that are close to what you searched for.
- Non-inclusive results.
By switching to ‘Verbatim’ all of these additional considerations are removed, and you will only see results that exactly match your search term.
The Knowledge Graph
Google search results are no longer just made up of paid and organic listings.
Google’s Knowledge Graph uses what it knows about a brand or website to enhance the search results. For example, if we search for Klood Digital we don’t just see our website at the top of the listings: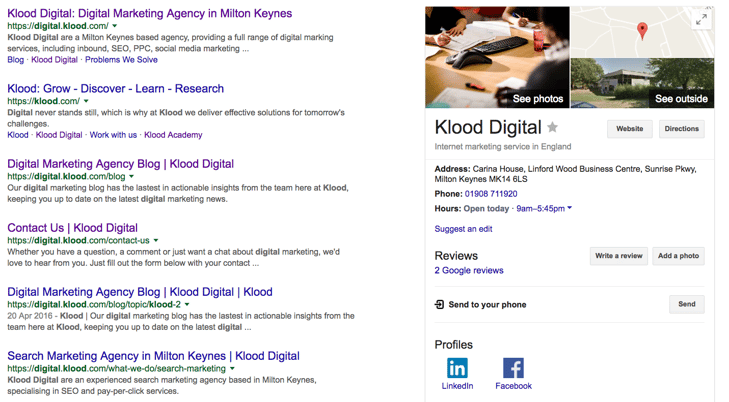
The Knowledge Graph adds information down the right-hand side, including pictures pulled through from our Google+ page, our address, phone number, opening times and links to our Facebook and LinkedIn profiles.
Instant Answers
Another new feature within Google’s SERPs that you’ve probably seen before are the Instant Answers. These are snippets of content that are pulled from ranking websites and displayed within the SERP itself.
Instant Answers are intended to give a quick answer to questions that have a verifiable answer, and also provide a link to the site where the information was taken from.
‘People also ask’
If you ask a question, for example ‘What’s wrong with my boiler?’, you may sometimes see a ‘People also ask’ box. This suggests some other questions that might be relevant to you.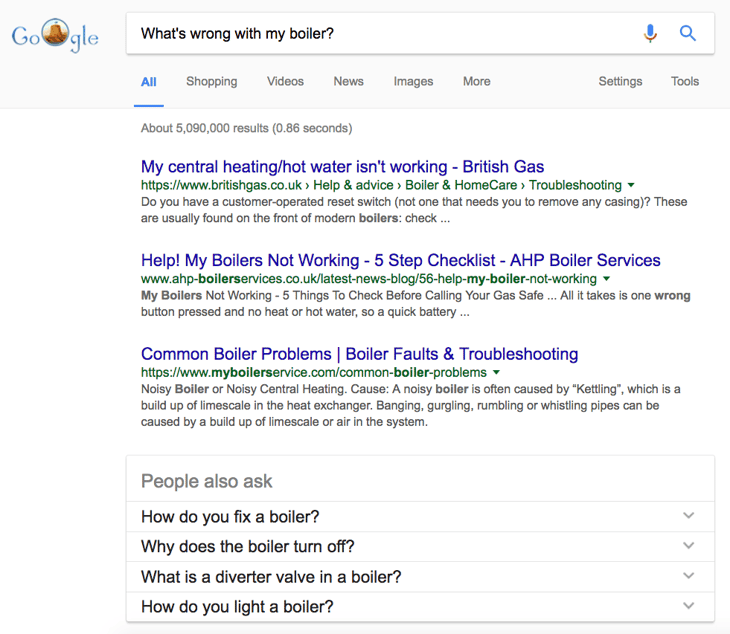
Click on one of the questions to expand the box and see an answer to the question.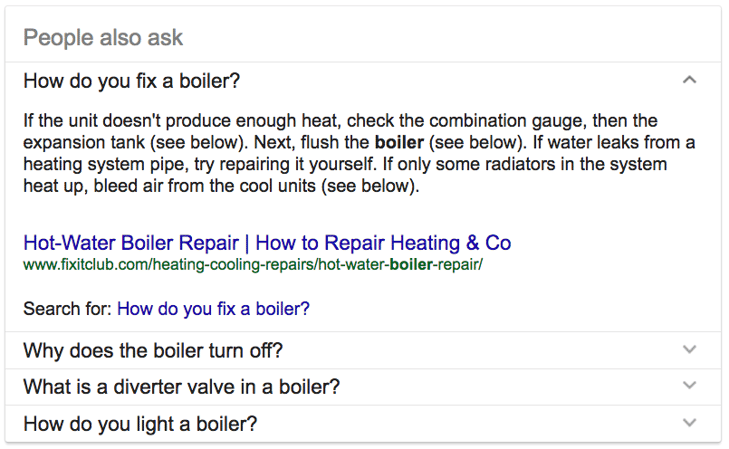
To read the whole article/web page, click on the link.
Featured snippets
Sometimes a question search will return a featured snippet, similar to that of one of the expanded ‘People also ask’ results: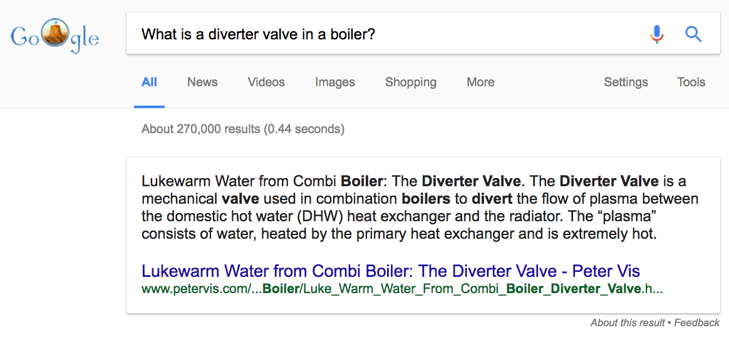
These are typically pulled through from one of the top ranking results, but there is no consensus in the SEO community about how Google’s algorithm chooses where to take the featured snippet from.
These are just the basics of what you’ll typically find within a Google search result page. There are more advanced features that we haven’t covered here, but this blog should’ve given you an idea about the different elements affecting your website listing’s click-through rate.
Our content includes affiliate links. This means that we may receive a commission if you make a purchase through one of the links on our website. This will be at no cost to you and helps to fund the content creation work on our website.